Can your body’s cell power plant ensure there is no shortage of electricity?
Activation of mitochondria brings sustainable and stable power supply.
Mitochondria are the "power plants" of cells, responsible for converting the food we consume into energy, producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy source required for cell operation. Mitochondrial activation is crucial for maintaining the body's health and vitality, especially for organs with high energy demands, such as the heart, muscles, and brain. When mitochondria function well, we can maintain stamina, concentration, and a healthy metabolism. Additionally, mitochondria participate in cellular antioxidant mechanisms, protecting cells from free radical damage and slowing down aging.
Modern lifestyles with fast pace and high work pressure often lead to mitochondrial dysfunction due to lack of exercise, unbalanced diets, and insufficient sleep. When mitochondria fail to generate enough energy, the body encounters numerous health issues, including chronic fatigue. Even after adequate sleep, one might still feel low in energy due to the inability to extract energy effectively from food. Metabolic problems, such as weight gain or difficulty losing weight, are also associated with mitochondrial energy deficiency, which hinders normal fat and carbohydrate metabolism. Long-term mitochondrial dysfunction accelerates cellular aging, increases free radical accumulation, and elevates risks for cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.

To maintain mitochondrial activity, lifestyle and dietary changes are essential. Regular, moderate exercise is one of the best ways to boost mitochondrial function, especially aerobic exercises and high-intensity interval training, which stimulate mitochondrial growth and activation. Studies have shown that regular exercise increases the number of mitochondria in cells and improves their efficiency in producing energy. Reducing stress and maintaining a good sleep routine are also critical, as stress generates free radicals that further damage mitochondria.

In terms of diet, consuming antioxidant-rich foods or functional supplements is vital for protecting mitochondria from oxidative damage. Ergothioneine, astaxanthin, vitamin C, vitamin E, S-adenosylmethionine, and Coenzyme Q10 are powerful antioxidants that help reduce free radical damage to mitochondria. Ergothioneine, in particular, is crucial as it enters cells via the OCTN-1 transporter, playing a key role in protecting mitochondria and ensuring proper energy conversion.
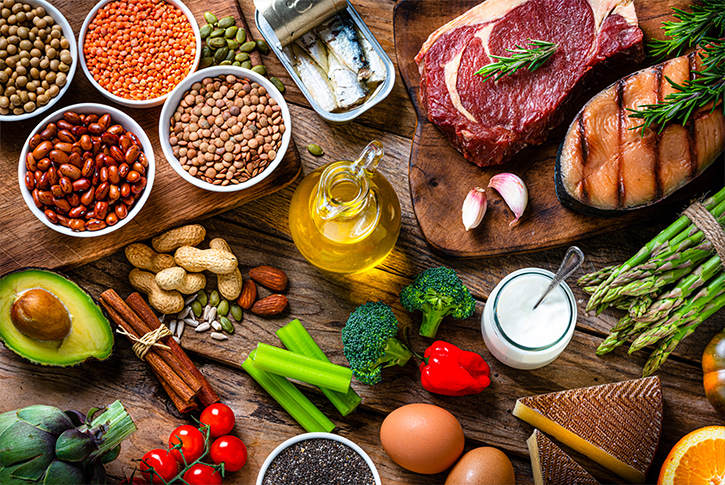

Furthermore, daily intake of Omega-3-rich foods like fish, flaxseeds, nuts, algae oil, and dark green vegetables promotes mitochondrial health by enhancing cell membrane structure and function while reducing inflammation. It's also recommended to avoid diets high in sugar and carbohydrates, as these can cause blood sugar fluctuations and increase insulin resistance, further impairing mitochondrial function. Opting for low-glycemic index whole grains helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduces the burden on mitochondria.
In summary, through exercise, a balanced diet, and antioxidant supplementation, we can effectively activate and maintain our mitochondria, preserving energy balance, slowing down aging, and preventing various metabolic and immune-related health issues. Mitochondrial health is the foundation of sustained energy and overall wellness.
